Practicing sports on a regular basis is a good way to maintain essential physical activity to improve health and prevent diseases. Many of the most prevalent diseases today are the result of a sedentary lifestyle and many of them improve with the practice of sports. Playing sports can help lower the risk of obesity and heart and metabolic diseases, improve high blood pressure, lower high levels of cholesterol and other fats in the blood and lower the risk of osteoporosis and keep muscles strong and flexible. In addition, exercise helps improve mood and self-esteem.
There is no reward without effort, and training and playing sports involve physical effort that sometimes has consequences and can cause discomfort, both physical and mental. Adequate nutrition, as has been said, is essential and there is nothing that can replace it. But knowing the dietary supplements that can help with certain problems and situations can be a great help, even in terms of performance
.
Sports performance and stress
Stress can affect our entire body, it acts differently on each person and begins with very different causes, such as: overwork, high physical exercise load, unbalanced diet, extreme temperatures, psychological pressure, etc.
 Sport is an activity in which challenges, physical overload and high commitment abound. Successful sports require technique and form, but it is also necessary to have skills for mental and emotional control. Depending on the characteristics of each sport, the physical conditions, as well as the challenges and limiting factors are different, but in all of them, one of the limiting factors that must be taken into account is stress, since these conditions can cause physical blockages (immobility, tension, stiffness, etc.), emotional (nerves, frustration, fear, etc.) and mental (thoughts of incapacity, surrender, etc.).
Sport is an activity in which challenges, physical overload and high commitment abound. Successful sports require technique and form, but it is also necessary to have skills for mental and emotional control. Depending on the characteristics of each sport, the physical conditions, as well as the challenges and limiting factors are different, but in all of them, one of the limiting factors that must be taken into account is stress, since these conditions can cause physical blockages (immobility, tension, stiffness, etc.), emotional (nerves, frustration, fear, etc.) and mental (thoughts of incapacity, surrender, etc.).
The management of stress and emotions in athletes is closely associated with their performance. Without an optimal emotional stress response, you cannot develop your full potential and you waste years of effort and chances of success.
Adaptogenic plants: what they are and how they can help
The term “adaptogen” was originally established by NV Lazarev in 1947 to define those substances believed to have the ability to normalize body functions and strengthen systems compromised by stress. Since it was not a single action, in 1969 Brekhman and Dardymov described the characteristics that a substance must have in order to be considered adaptogenic. According to these authors, a substance to be considered adaptogenic must meet the following conditions:
a) It must not be toxic to the recipient.
b) It is not specific in its pharmacological properties and acts by increasing the bodys resistance to a wide range of adverse factors: chemical, physical and biological.
c) It tends to be a regulator that has a normalizing effect on the various systems of the recipient organism.
The main characteristic of adaptogens is that they help the body to help itself. Because adaptogens restore functions affected by stress, the perceived impact depends on the type of stress you are exposed to. In sports practice, studies suggest that adaptogens have the following applications:
- They can restore and improve physical and mental energy.
- They help improve physical and mental endurance.
- They help reduce anxiety.
- They have a wider effect than antioxidants: they can protect against different substances that can be harmful to cells, including free radicals.
- They help, therefore, to maintain high levels of physical and mental performance.
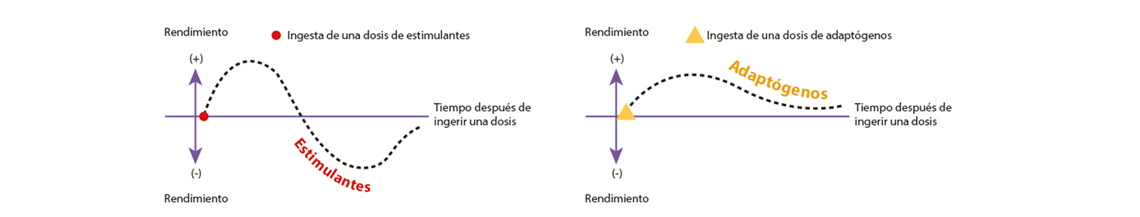
Adaptogens vs. stimulants
The difference between stimulants, such as coffee, tea or energy drinks, and adaptogens, is that stimulants provide a “high” even when you are in balance. But the stimulus is relatively short and, if excessive, could cause side effects such as increased heart rate, sweating and sleep disorders, as well as a greater degree of subsequent fatigue. Adaptogens, however, can provide a milder effect for a longer time while helping to sharpen the senses and improve abilities
.
Among the plants whose actions make it possible to classify them within the group of adaptogens, the most used are: Ashwagandha, Schisandra, Rhodiola, Eleutherococcus.
Ashwagandha (Whitania somnifera L.), also known as Winter Cherry for its bright red fruit, is a woody shrub native to India. In Ayurvedic culture, for 3000 years, they have used their roots and leaves as support during situations of acute stress. Ashwagandha helps maintain emotional stability, being very useful in cases of temporary stress. It helps maintain physical and mental well-being.
The Schisandra (Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill.) is a deciduous and climbing shrub whose berries are used as a tonic and restorative, can help a persons ability to adapt to stress, and contribute to the recovery of physical and mental well-being
.
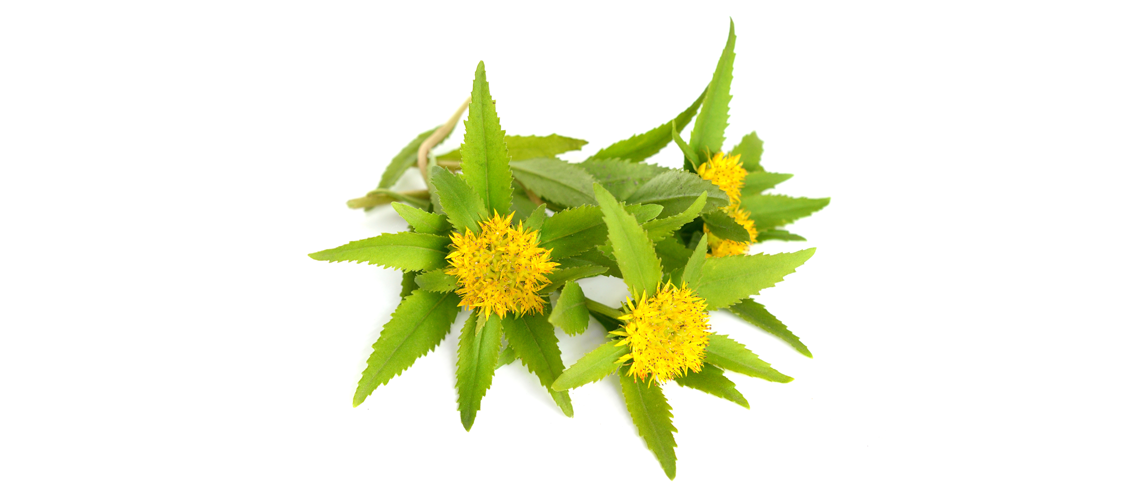
 Rhodiola (Rhodiola rosea L.) is a plant native to the cold regions of the planet, which is why it is also called polar rose. Its roots go back thousands of years: the ancient Greeks already used this plant, the Russians administered it to their athletes and soldiers, and even the Vikings used it regularly. Rhodiola helps to adapt to emotional stress and physical exertion. It has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, helping to protect against stress. It also has a beneficial effect on fatigue.
Rhodiola (Rhodiola rosea L.) is a plant native to the cold regions of the planet, which is why it is also called polar rose. Its roots go back thousands of years: the ancient Greeks already used this plant, the Russians administered it to their athletes and soldiers, and even the Vikings used it regularly. Rhodiola helps to adapt to emotional stress and physical exertion. It has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, helping to protect against stress. It also has a beneficial effect on fatigue.
Eleutherococcus (Eleutherococcus senticosus Maxim.) is a plant that grows spontaneously on the slopes of the mountains of Siberia. Its roots have compounds that help maintain high levels of physical and mental energy, supporting physical and intellectual capacities in case of exhaustion
and tiredness.
Some articles point out that adaptogenic plants work best when combined with each other. They have a synergistic effect between their components in which it is achieved that 1 + 1 is not 2, but 3. It has been demonstrated that by combining different adaptogenic plants in appropriate proportions, the individual effect of each plant is enhanced
.
El Maral and B vitamins
The Maral (Rhaponticum carthamoides (Willd.) Iljin.) is a herbaceous plant of the Compositae family, native to China, Kazakstan, Siberia and Mongolia. It has made its place in sports medicine due to its adaptogenic properties thanks to the phytoecdysteroids found in its root. Maral contributes to the adaptation to stress and to the capacity for mental work
.
Certain B vitamins are also interesting in sports:
- Thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), pantothenic acid (B5) and pyridoxine (B6) contribute to normal energy metabolism.
- Riboflavin (B2), pantothenic acid (B5) and pyridoxine (B6) help reduce tiredness and fatigue.
- Pantothenic acid (B5) contributes to normal intellectual performance and to the normal synthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones such as cortisol, as well as to reducing tiredness and fatigue.
To conclude the article, it is important that all dietary supplements used in sports ensure the absence of substances prohibited in sports. It is necessary that each batch of a certain product be analyzed by an authorized laboratory of the WADA (World Anti-Doping Agency) to ensure the quality and reliability of the
product.
Paula Saiz

• Degree in Biological Sciences from the Complutense University of Madrid, specializing in plant biology.
• Master in Applied Plant Biology from the Complutense University of Madrid.
• Collaboration in the Endothelial Pathology Unit of the Ramón y Cajal Hospital in Madrid: clinical trials and anti-aging phytotherapy.
• He is currently part of the Department. 100% Natural Technical and Documentation and Training.
All rights reserved ©. The reproduction, partial or total, of the content in any form is prohibited without the prior written consent of Cien Por Cien Natural SL. If you want to share the information, reproduction is allowed by citing Cien Por Cien Natural SL or using the link on their website. Cien Por Cien Natural SL is not responsible for misuse of the content of the article
.